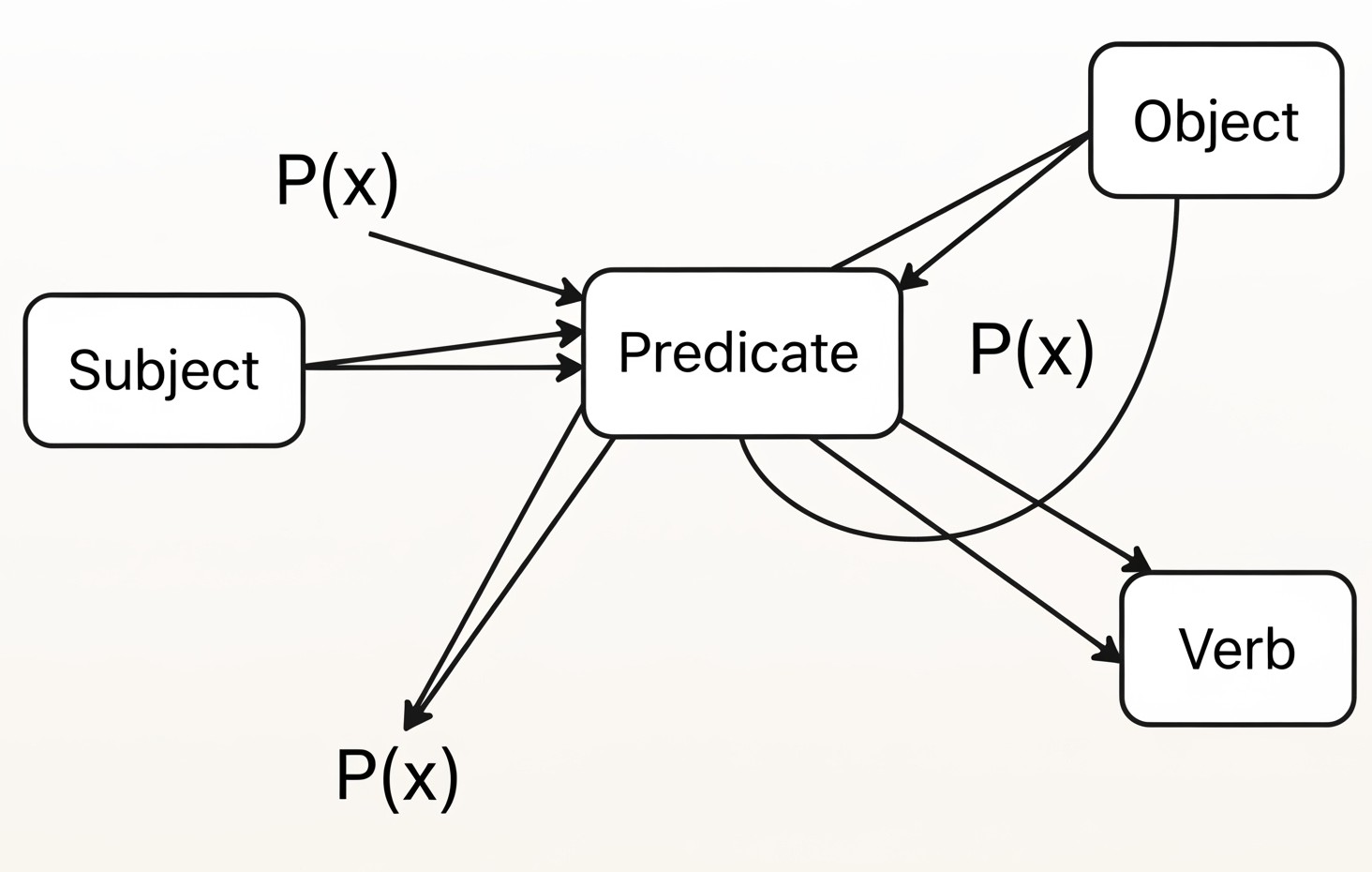
“Decision Tree”は汎用性のあるデータ構造で、”series of predicates” — つまり (x<2, y>=0.4, z="ABC", …)のようなもの — をnodeとして含めることができます1。
勿論、データとして含めるだけであればfulltextで構わないのですが、或る程度のデータ量になるとパフォーマンスの影響が深刻になり、何よりも演算による構造の消失 (互換性が無い) やpredicate特有の演算 (少なくともunion及び intersection) を利用できない致命的な問題があります。
6月7日時点のリサーチでは、Postgreの実装では次のようなものが挙がっています。
ltree(label tree)R-trees(GiSTextensionとして実装)k-d tree(SP-GiSTextensionとして実装)Generalized Search Tree(GiST)
一つ一つ解説していきましょう。
Label Tree
ltreeはTree構造をLabelで表現したものです。公式の例を見ると、次のような構成により、後続のTree構造が導出されるようなものです。
CREATE TABLE test (path ltree);
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Science');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Science.Astronomy');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Science.Astronomy.Astrophysics');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Science.Astronomy.Cosmology');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Hobbies');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Hobbies.Amateurs_Astronomy');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections.Pictures');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections.Pictures.Astronomy');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections.Pictures.Astronomy.Stars');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections.Pictures.Astronomy.Galaxies');
INSERT INTO test VALUES ('Top.Collections.Pictures.Astronomy.Astronauts');
CREATE INDEX path_gist_idx ON test USING GIST (path);
CREATE INDEX path_idx ON test USING BTREE (path);
CREATE INDEX path_hash_idx ON test USING HASH (path); Top
/ | \
Science Hobbies Collections
/ | \
Astronomy Amateurs_Astronomy Pictures
/ \ |
Astrophysics Cosmology Astronomy
/ | \
Galaxies Stars Astronautsこれは(series of) predicatesとしては弱く、「各項目が所定のLabelに所属するかどうか」を返す評価関数と解釈できるものの、次のような弱点があります。
- 原則Categoricalな値に限定される;2
- 1と類似していますが、表現可能なpredicateが「定義済みLabelへの所属」のみ.
R-tree & k-d tree
これらの(Postgre)実装は、ltreeと同様、indexing mechanismや演算だけでなく、GEOMETRYという型を提供しています。そうする事で、対象のk-Neighborsを効率的に算出する為の空間分割と、分割空間における位相的演算が可能になっています。
有用な適用範囲としては、Continuous値か、Categorical値であってOrdinal (順序付き)なものに限られます。
predicatesの解釈としては、 (x_min<=x<=x_max, y_min<=y<=y_max, ...)のような範囲型の評価に適しています。
以下はユースケースによる比較です。
GiST (R-tree) vs. SP-GiST (k-d Tree/Quad-tree)
| Feature | GiST (R-tree) | SP-GiST (k-d Tree / Quad-tree) |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | General purpose spatial data. Handles points, lines, and polygons, including overlapping data. | Point data. Particularly non-overlapping data points. |
| Structure | Bounding boxes that can overlap. More flexible. | Rigid partitions of space (quadrants). No overlaps. |
| k-NN Search | Good. The <-> operator3 is supported and works well. | Excellent. Generally faster for k-NN on point clouds. |
| Use Case | Finding parks that intersect a road, cities within a state, any geographic feature search. | Finding the nearest taxis, sensors, or ATMs to a user. |
Generalized Search Tree (GiST)
PostgreSQLのGiSTのフレームワークは、カスタム型やそのindexing mechanism、operatorを実装するツールキットを提供しており (c.f. 64.2. GiST Indexes, 68.3. Extensibility)、自由度が極めて高くPredicate Modelも実装できるはずです(Cで書く必要があり、明らかに大仕事)。
参考までに、実装には「カスタム型」を構成する
- type
- index
- operation
を規定する為に以下7つの関数を与える必要があります。
consistent: Determines if a query is consistent with an index entry.
union: Merges information from several tree entries.
compress: Converts a data item into a format suitable for storage in an index page.
decompress: The reverse of compress.
penalty: Calculates the "cost" of inserting a new entry into a particular subtree.
picksplit: Decides how to split a set of entries when an index page overflows.
same: Checks if two index entries are identical.総括
形式論理をNeural Networkの途中生成物や、直接的に概念の抽象モデルとして利用するアプリケーション (e.g., プログラミング言語, 証明支援システム)は、そのアイデア自体が目新しいという訳ではなく、少なくとも人工知能(AI)研究の黎明期 — 人間の思考を論理記号で表現しようとする記号主義AI (Symbolic AI) が主流であった時代 — に遡ります。
同時期の1940年代には、McCulloch-Pittsが形式ニューロン4を提唱し、AIとNeural Networkには密接な関わりがあったことが推測されます。
“predicate” のデータモデルとしての印象 — 万能で豪華である — は、その表現力と解釈可能性から来るものなのですが、近年のアカデミックな文脈では、predicate logicを”表現”として媒介する事で推論能力を向上させたり、その形式性から意味論上の分散を小さく抑える等の研究があるようです(以下参考)。
- A Data Model and Predicate Logic for Trajectory Data
- Predicate Logic as a Modeling Language: Modeling and Solving some Machine Learning and Data Mining Problems with IDP3
- Entailment-Preserving First-order Logic Representations in Natural Language Entailment
- Unsupervised Grounding of Plannable First-Order Logic Representation from Images
- Grounded Chain-of-Thought for Multimodal Large Language Models
- Theory reconstruction: a representation learning view on predicate invention